The PCOS and Prolactin Connection
PCOS is characterized by an array of symptoms that range from menstrual and infertility issues to obesity and excessive hair growth. These don’t seem to connect logically but when viewed together they can point to Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, which affects between 5-10 percent of all women.7 PCOS is not the only condition that can cause these types of menstrual irregularities or infertility but it is the most prevalent along with high prolactin levels.6 High prolactin levels have many of the same symptoms as PCOS and needs to be ruled out using a blood test to be certain of a PCOS diagnosis.4
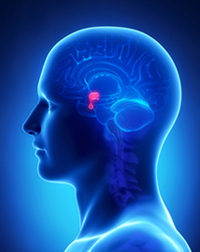 Prolactin is a hormone whose primary function is to initiate lactation. It is released by the pituitary gland, a small organ located at the base of the brain that influences the entire body. The pituitary gland produces prolactin and a number of other key hormones including growth hormone, luteinizing hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, and adrenocorticotropin hormone.2 Excessive prolactin can cause a decrease in sex hormones like estrogen. When you have excessive amounts of prolactin in your blood it is called hyperprolactinemia. This is sometimes a marker of a condition known as prolactinoma, which is a tumor of the pituitary gland (usually non-cancerous). Prolactinomas produce higher than normal levels of prolactin, which can wreak havoc on the body and produce many PCOS-like symptoms.
Prolactin is a hormone whose primary function is to initiate lactation. It is released by the pituitary gland, a small organ located at the base of the brain that influences the entire body. The pituitary gland produces prolactin and a number of other key hormones including growth hormone, luteinizing hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, and adrenocorticotropin hormone.2 Excessive prolactin can cause a decrease in sex hormones like estrogen. When you have excessive amounts of prolactin in your blood it is called hyperprolactinemia. This is sometimes a marker of a condition known as prolactinoma, which is a tumor of the pituitary gland (usually non-cancerous). Prolactinomas produce higher than normal levels of prolactin, which can wreak havoc on the body and produce many PCOS-like symptoms.
Causes
How Did You Get PCOS?
 Quite a few medical professionals think several factors, such as genetics, are variables in the development of polycystic ovarian syndrome.6 If your sister or mother has PCOS, your risk of also having it increases. Hormone imbalance is definitely a major influencing element in PCOS, together with a condition known as Insulin Resistance.7 Insulin is a powerful hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin transfers sugar out of the blood and moves it into other cells. The sugar is then stored as fat or converted into energy. When this complex process malfunctions it is called Insulin Resistance. For those who have Insulin Resistance the pancreas releases over-excessive amounts of insulin to eliminate sugar from the blood. Higher than normal levels of insulin are not beneficial to the body and often create a confusing assortment of symptoms. Insulin Resistance is extremely prevalent in women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and many symptoms of PCOS stem from Insulin Resistance.6
Quite a few medical professionals think several factors, such as genetics, are variables in the development of polycystic ovarian syndrome.6 If your sister or mother has PCOS, your risk of also having it increases. Hormone imbalance is definitely a major influencing element in PCOS, together with a condition known as Insulin Resistance.7 Insulin is a powerful hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin transfers sugar out of the blood and moves it into other cells. The sugar is then stored as fat or converted into energy. When this complex process malfunctions it is called Insulin Resistance. For those who have Insulin Resistance the pancreas releases over-excessive amounts of insulin to eliminate sugar from the blood. Higher than normal levels of insulin are not beneficial to the body and often create a confusing assortment of symptoms. Insulin Resistance is extremely prevalent in women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and many symptoms of PCOS stem from Insulin Resistance.6
What Else Could Your Symptoms Be?
You might already have a diagnosis of PCOS, but what if your symptoms are caused by another condition altogether. There is a very good chance your doctor might have mentioned looking at your prolactin levels before settling on Polycystic 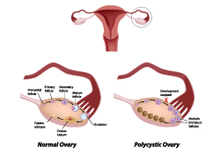 Ovarian Syndrome. Raised levels of prolactin (hyperprolactinemia) and PCOS are the most common conditions that cause menstrual irregularities.5 Women with PCOS occasionally have mildly elevated prolactin levels and there is a school of thought that these two conditions might be connected in some way.
Ovarian Syndrome. Raised levels of prolactin (hyperprolactinemia) and PCOS are the most common conditions that cause menstrual irregularities.5 Women with PCOS occasionally have mildly elevated prolactin levels and there is a school of thought that these two conditions might be connected in some way.
What Causes Hyperprolactinemia?
Elevated prolactin levels can present from slightly to extremely over normal and can be caused by several factors such as:
- A tumor on the pituitary gland called a prolactinoma. This is a common cause of hyperprolactinemia and usually the most serious.8
- Certain prescription medicines for:
 Depression
Depression- Heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Pain
- High blood pressure
- Ulcers
- Mental health disorders
- Menopause
- Hypothyroidism – The thyroid gland is not producing enough thyroid hormone.9
- Other tumors on the pituitary gland.
- Diseases that affect the pituitary gland.
- Chronic liver disease.
- Radiation treatment for tumors near or on the pituitary gland.
- Chronic kidney disease.
- Chest-wall injuries.
- Conditions like shingles that affect the chest wall.
- Breast stimulation.
- Intercourse.
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome.4
What Causes a Prolactinoma?
The cause of pituitary tumors, such as a prolactinoma, is basically unknown, although some factors seem to increase the risk.8 Prolactinomas are extremely rare and usually occur in women between 20 and 50 years old. Individuals  can have a genetic predisposition for developing these types of tumors and often you will find a family relation with a prolactinoma.8 Another factor could be a genetic disorder called Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1, a condition characterized by abnormal hormone production from the pituitary gland, pancreas, and parathyroid.9 Unfortunately, most prolactinomas occur without any underlying cause, which makes it hard to anticipate or diagnose without tests.
can have a genetic predisposition for developing these types of tumors and often you will find a family relation with a prolactinoma.8 Another factor could be a genetic disorder called Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1, a condition characterized by abnormal hormone production from the pituitary gland, pancreas, and parathyroid.9 Unfortunately, most prolactinomas occur without any underlying cause, which makes it hard to anticipate or diagnose without tests.
Symptoms
What Does PCOS and Hyperprolactinemia Look Like?
The symptoms we experience, whether from PCOS or hyperprolactinemia, are what ultimately send us to the doctor to get relief or simply peace of mind. The cause of the condition is often secondary for people because the physical symptoms reduce our quality of life. It is very important to write down your symptoms (including frequency, time, and severity) so you can give an accurate and comprehensive description of what is going on in your body. This will help your doctor make the right diagnosis or at least order the right tests. Since Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and hypoprolactinemia look similar, this list of symptoms is crucial to rule out one or the other.5
The ways that Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome shows itself can include:7
- Absent periods
- Irregular periods
- Heavy periods
- Excessive period cramps
- Increased facial and body hair (hirsutism)
- Obesity
- Acne
- Dandruff
- Dark patches on the skin
- Male pattern baldness
- Ovarian cysts
- Infertility
- Painful intercourse
The majority of women with PCOS will have some sort of menstrual issue and hormone imbalance. Many will also have Insulin Resistance and be obese.6 Although these symptoms are not unique to women with PCOS, the various combinations of the symptoms defines Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome.
Hyperprolactinemia also has several symptoms which when looked at together can point your physician toward this disorder. Symptoms of hyperprolactinemia might be nonexistent or women may notice the following:9
 Absent periods
Absent periods- Irregular periods
- Heavy periods
- Milky discharge from the breasts (galactorrhea)
- Infertility
- Headaches
- Loss of interest in sex
- Painful intercourse due to vaginal dryness
Some possible complications associated with having a prolactinoma are:
- Vision loss:? This will usually only occur when the prolactinoma untreated and it grows large enough to compress the optic nerve. If this happens surgery is sometimes the only option to provide relief.8
- Bone loss:? If you have too much prolactin in your blood this will often decrease the amount of estrogen, which can result in bone density decreasing as well. This condition is called osteoporosis and can be very debilitating.
- Hypopituitarism:? If there is a tumor on your pituitary gland and it grows large enough to put pressure on the gland it can impede its function. This can mean other hormones controlled by the pituitary gland are imbalanced, causing conditions like adrenal insufficiency, deficiency in growth hormone and hypothyroidism.9
- Pregnancy issues:? Pregnancy naturally increases prolactin production and the added stress of having a prolactinoma on the pituitary gland can send prolactin levels through the roof. This can cause visual disturbances and headaches.8
 It should be obvious that the symptoms of PCOS and hyperprolactinemia are very similar and could possibly be confused with each other.1 Making a definitive diagnosis of PCOS or hyperprolactinemia is crucial because they are caused by different factors and need to be treated differently to provide relief from symptoms. Some women with PCOS also have high prolactin levels and there might be some sort of connection between the two conditions that has not yet been established.5 The only way to get the right diagnosis is tests and procedures designed to pinpoint markers of both conditions.
It should be obvious that the symptoms of PCOS and hyperprolactinemia are very similar and could possibly be confused with each other.1 Making a definitive diagnosis of PCOS or hyperprolactinemia is crucial because they are caused by different factors and need to be treated differently to provide relief from symptoms. Some women with PCOS also have high prolactin levels and there might be some sort of connection between the two conditions that has not yet been established.5 The only way to get the right diagnosis is tests and procedures designed to pinpoint markers of both conditions.
How Can You Tell the Difference Between the Two Disorders?
PCOS is diagnosed using the presenting symptoms and sometimes the appearance of the woman. Ordinarily a woman has to have at least two of the common symptoms of PCOS to consider this disorder as a possibility.7 There are also some tests or procedures that can be done to eliminate a condition like prolactinemia because it can present in such a similar fashion and PCOS hormone combinations are quite different than those connected to prolactinemia. These tests include:
- Blood tests:? these will check several things in the body.8
- Female sex hormones
- Prolactin levels
- Male sex hormones
- Glucose
- Thyroid function
- Other hormones
- Ultrasound:? this can be used to determine the presence of ovarian cysts and what they look like in the ovary. Women with PCOS have ovaries that look like they are filled with tiny holes.3
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):? If PCOS is ruled out and you have hyperprolactinemia your doctor will look at your thyroid levels to determine whether the high prolactin levels are caused by hypothyroidism. If your thyroid hormones are normal an MRI could be ordered to look for evidence of a tumor.9
Treatment Options
Medical Treatment Options for PCOS Hormonal Imbalance
What can you expect when being treated for a prolactinoma?
Prolactinomas can be classified according to their size (less than 1 cm are microadenomas and over 1 cm are macroadenomas)8, and this classification can determine the type of treatment that is recommended. Your first option is usually medication, because if the tumor is not pressing on other tissue or nerves most doctors will avoid an invasive surgical procedure.
The treatment goals for a prolactinoma are usually are straightforward, such as returning your prolactin levels to normal and shrinking the tumor. Indirectly by doing these things you will also get relief from symptoms of the tumor, like vision disturbances, and have normal pituitary function restored.9
What Medications are Used to Treat Prolactinomas?
There are several oral medications that have been quite successful in shrinking the tumor associated with this condition and lowering prolactin levels. Medication for this health issue is often considered to be a long-term solutions, and dopamine agonists are considered the best option. The brain chemical that manages the production of prolactin is called dopamine, and these drugs mimic that chemical.8 Some common dopamine agonist drugs used to treat prolactinomas are:
 Bromocriptine: ?This drug is quite effective for reducing prolactin levels but should be taken continuously because when it is discontinued the levels can rise again. The dose of this drug should be increased gradually so side effects like nausea don’t become debilitating.2
Bromocriptine: ?This drug is quite effective for reducing prolactin levels but should be taken continuously because when it is discontinued the levels can rise again. The dose of this drug should be increased gradually so side effects like nausea don’t become debilitating.2- Cabergoline: ?This drug is often used as a last resort because it is expensive and linked to several adverse side effects.2
Side effects – Most medications cause side effects and sometimes the list seems longer than the symptoms you are trying to eliminate! Luckily you might be able to stop taking the drugs used to treat a prolactinoma if the tumor shrinks and your prolactin levels returns to normal for at least two years. Some common side effects of the medications used to treat a prolactinoma are:8
- Lightheadedness
- Nasal congestion
- Nausea
- Heart valve damage (Cabergoline)
Surgical Treatments
Surgery might be a choice if medications do not help or you have an adverse reaction to the recommended drugs. You might  have to have surgery if there is pressure on your nerves affecting your vision. The type of surgical intervention will depend on the size and location of the tumor.
have to have surgery if there is pressure on your nerves affecting your vision. The type of surgical intervention will depend on the size and location of the tumor.
- Transsphenoidal surgery: This is the most commonly performed surgery for prolactinomas and the least invasive because the tumor is removed via the nasal cavity. It leaves no visible scars and has the least risk.9
- Transcranial surgery: If you have a large tumor that appears to be spreading to the adjacent tissues you might need a more invasive surgery called a craniotomy. The tumor is accessed through the skull during this procedure.9
Radiation
If surgery is not an option and you are not responding well to medication your doctor might recommend radiation therapy. This is usually only offered after every other option is exhausted.8
Natural Therapies
Can You Treat Prolactinemia without Medication?
Natural treatment options are a crucial component in PCOS and prolactinemia. Diet, exercise, and nutritional supplements are the foundation of most PCOS management plans designed to reverse hormonal imbalances and address PCOS.7 These components can also help hyperprolactinemia.
Diet
Diet is a treatment component entirely within your control, and you are 100 percent responsible for its success or failure. This can be a little scary because on the whole it is easier to take a pill than plan a meal. If you are not inclined to be experimental in the kitchen, do not despair because diets designed to treat both PCOS and prolactinemia contain many familiar foods and preparations. You do not have to trek down to the gourmet store or wander the aisles in your local Chinese grocery to find ingredients. Some simple guidelines to follow to help lower your prolactin levels are:1
- Try to eat foods that are natural and without preservatives.
- Include many fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Eat an abundance of dark leafy greens.
- Try to eat as many whole grains as possible.
- Eat soybeans, nuts, and legumes.
- Eat foods containing vitamin B6 because there is a link between hyperprolactinemia and vitamin B6 deficiency. These foods include spinach, bananas, chicken, and wild-caught salmon.
- Include foods high in zinc, such as beans, shellfish, and turkey because zinc supplements have been found to decrease prolactin.
- Avoid caffeine, alcohol, white sugar, and artificial sweeteners.
Nutritional Supplements
 The use of botanicals to manage various conditions, symptoms, and diseases goes back centuries. You already might be using a natural remedy if you have Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome to reverse hormone imbalance, improve menstrual irregularities, and respond to your Insulin Resistance.1 One of the most common botanical ingredients found in Nutritional Supplements targeted for PCOS is a plant native to the Mediterranean called Chaste Berry or Vitex. It is very effective for any kind of hormonal imbalance and can work to help bring prolactin back to normal levels in the blood.1 Chaste Berry Nutritional supplements can be found as capsules, pills, and liquid extracts. This is also considered the best botanical for high prolactin levels because it can prevent the release of prolactin by binding to the dopamine receptors.1 The effects of Chaste Berry are often not noticeable for several months but eventually you should see improvements in both PCOS symptoms and hyperprolactinemia.1 Always consult your physician before trying a natural remedy like Chaste Berry.
The use of botanicals to manage various conditions, symptoms, and diseases goes back centuries. You already might be using a natural remedy if you have Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome to reverse hormone imbalance, improve menstrual irregularities, and respond to your Insulin Resistance.1 One of the most common botanical ingredients found in Nutritional Supplements targeted for PCOS is a plant native to the Mediterranean called Chaste Berry or Vitex. It is very effective for any kind of hormonal imbalance and can work to help bring prolactin back to normal levels in the blood.1 Chaste Berry Nutritional supplements can be found as capsules, pills, and liquid extracts. This is also considered the best botanical for high prolactin levels because it can prevent the release of prolactin by binding to the dopamine receptors.1 The effects of Chaste Berry are often not noticeable for several months but eventually you should see improvements in both PCOS symptoms and hyperprolactinemia.1 Always consult your physician before trying a natural remedy like Chaste Berry.
References
-
Hyperprolactinemia. The Herbal Physician. [Online] [Cited: 07 24, 2012.] http://theherbalphysician.com/hyperprolactinemia.html.
- Hyperprolactinemia. John Hopkins. [Online] [Cited: 07 24, 2012.] http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/neurology_neurosurgery/specialty_areas/pituitary_center/conditions/hyperprolactinemia.html.
- Norman RJ, Dewailly D, Legro RS, Hickey TE. Polycystic ovary syndrome. Lancet. 2007 Aug 25;370(9588): pp 685-97.
- Cahill, Dr David. PCOS. Net Doctor. [Online] 01 15, 2010. [Cited: 07 23, 2012.] http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/womenshealth/facts/pcos.htm.
- Sterling, E. Hormone Levels and PCOS . OBGYN Net. [Online] 11 11, 2011. [Cited: 07 23, 2012.] http://hcp.obgyn.net/polycystic-ovary-syndrome/content/article/1760982/1985987.
- Debbie Bridges, MD . Infertility and Reproduction. WebMD. [Online] 03 12, 2010. [Cited: 07 18, 2012.] http://www.webmd.com/infertility-and-reproduction/guide/absence-periods.
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS). American Diabetes Association. [Online] [Cited: 07 18, 2012.] Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS).
- Esther Eisenberg, M.D., M.P.H. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) fact sheet. Womens Health. [Online] 03 17, 2010. [Cited: 07 18, 2012.] http://www.womenshealth.gov/publications/our-publications/fact-sheet/polycystic-ovary-syndrome.cfm.
- Mayo Clinic Staff. Prolactinoma. Mayo Clinic. [Online] 05 16, 2012. [Cited: 07 23, 2012.] http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/prolactinoma/DS00532.
- Robert Ferry Jr, MD. Prolactinoma. Medicine Net. [Online] [Cited: 07 23, 2012.] http://www.medicinenet.com/prolactinoma/page7.htm.
Next Steps
- Take the PCOS Quiz! Get your score and assess your hormone health risks.
- Join our Facebook Sisterhood Group Pose your questions to this group of like-minded women. Get the answers to your questions and the support you need.
- Checkout the Hormone Reset. Guided Practices to eliminate anxiety, lose weight and boost energy.
We are committed to helping women reverse their symptoms of hormone imbalance – a major cause of excess weight gain, adult acne, unwanted facial hair, depression, anxiety, and heartbreaking female infertility.
©Insulite Health empowers women with hormone imbalance to transform their lives through a process of healing with the Natural Hormone Solution –a complete solution for helping women reverse the symptoms hormone imbalance..


 Depression
Depression Absent periods
Absent periods Bromocriptine: ?This drug is quite effective for reducing prolactin levels but should be taken continuously because when it is discontinued the levels can rise again. The dose of this drug should be increased gradually so side effects like nausea don’t become debilitating.2
Bromocriptine: ?This drug is quite effective for reducing prolactin levels but should be taken continuously because when it is discontinued the levels can rise again. The dose of this drug should be increased gradually so side effects like nausea don’t become debilitating.2